Saving and investing are great ways Canadians can improve their finances and build wealth. The tax-free savings account helps to achieve these financial goals.
Here’s everything you should know about the tax-free savings account: what it is, how to open one, withdrawal rules, and what investment assets you can hold.
The Tax-Free Savings Account
More widely known as the TFSA, the tax-free savings account is a registered account the Canadian government created to incentivize Canadians to save. The biggest catch to the TFSA is that you can earn tax-free investment income.
When you invest outside of a registered account in Canada, the Canada Revenue Agency will tax any dividends or capital gains you make. Through your TFSA, these earnings are not taxed.
For example, if you buy an investment asset, such as a stock, in a non-registered account for $1,000 and sell it after a few months for $1,500, you will make a capital gain of $500.
The CRA will tax half of your gains ($250) at your marginal tax rate. If your tax rate is 20%, you will pay $50 tax, which is 20% x $250.
Suppose you invested your $1,000 in a TFSA, the CRA will not tax your capital gains. You get to keep all of it to yourself.
What is the TFSA limit?
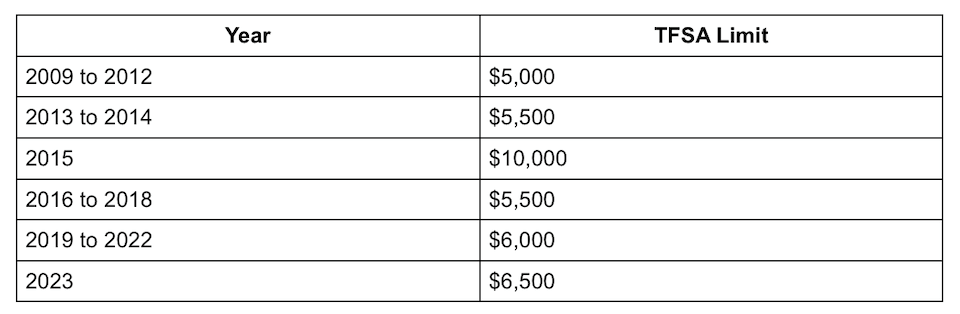
Since 2009 when the Canadian government introduced the tax-free savings account, they have restricted the maximum amount each Canadian can contribute to the TFSA each year.
The CRA tries to increase the TFSA limit based on the inflation rate. For example, due to high inflation rates in 2022, the CRA increased the tax-free savings account contribution limit from $6,000 to $6,500 in 2023.
Here is a breakdown of the TFSA limit since 2009.
The TFSA contribution room is a cumulation of all your unused TFSA limits from when you become eligible to open an account. You can carry the limit amount forward if you do not use your contribution room in any given year.
Assume you became eligible to open a tax-free savings account in 2019 but have yet to contribute any amount. Your available contribution room is the sum of the TFSA limits for all the years from 2019 to 2023, which is $30,500.
If you contribute above your TFSA limit for any reason, you will pay a 1% tax on the excess amount for every month it remains in the account. It is your responsibility to track your available TFSA contribution room.
You can find your TFSA contribution room in your CRA My Account profile.
Your financial institution will report any contributions and withdrawals to the Canada Revenue Agency. If there are any discrepancies, you can contact your financial institution and the CRA to correct any errors.
How do you open a TFSA account?
To open a Tax-free savings account and enjoy the tax savings benefits, you must be a Canadian resident and at least 18 years old. You must be 19 years old in British Columbia to get into a TFSA contract. However, your TFSA limit starts counting from when you are 18, and you can carry it forward.
For example, if you turned 18 in 2022, when you become eligible to open a TFSA by the time you turn 19, your total TFSA contribution limit will be $12,500.
Most financial institutions offer the tax-free savings account. You can walk into a physical branch or call the financial institution for assistance. Some financial institutions allow you to open a TFSA online.
Financial institutions in Canada that offer the TFSA include banks, credit unions, investment companies, trusts, and insurance companies.
You can also open a tax-free savings account with a brokerage and manage a self-directed TFSA. Some financial institutions offer the TFSA through Robo-advisors. If you open a tax-free savings account with a Robo-advisor, you will get a semi-managed account with minimal investment support.
Through your TFSA, you can invest and grow your savings. Allowable investment assets include stocks, bonds, guaranteed investment certificates (GICs), mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and real estate investment trusts (REITs).
Investing in non-allowable assets, such as cryptocurrency, through your TFSA can attract penalties and fees.
Tax-Free Savings Account withdrawal rules
There are no restrictions for withdrawing from your TFSA account. You can withdraw your funds from a tax-free savings account at any time. Some financial institutions charge fees for selling financial assets in a TFSA or transferring your account to another financial institution.
You can also use the money in your TFSA for any reason. This can include buying a house, paying for school expenses, saving for retirement, and travelling, among other reasons.
However, when you withdraw from your TFSA, you do not get the contribution room back until the following year.
Summary: Key takeaways about Tax-Free Savings Accounts
The tax-free savings account is a great financial tool for every Canadian. While this account is called a savings account, you can use it to invest. Use a TFSA to start saving and investing to grow wealth.
It does not matter if you do not know how to invest yet. You can open a TFSA with a financial institution that offers this account, and they can manage your investments for you.
You have access to your funds in a TFSA at any time, but make sure to read your contract to understand any fees for selling an investment asset.




